高级命令
wc
[root@localhost ~]# wc -l /etc/passwd -l 行数
[root@localhost ~]# wc -c aa.txt -c 字符数
[root@localhost ~]# wc -w /root/aa.txt -w 以空格分隔连续的字符串
上下颠倒(逆序)
[root@localhost ~]# cat -n /etc/passwd | tac
左右颠倒(镜像)
[root@localhost ~]# cat -n /etc/passwd | rev
cut 截取
[root@localhost ~]# cut -d":" -f 1 /etc/passwd -d 分隔符 -f 字段
[root@localhost ~]# cut -d":" -f 1,3,6 /etc/passwd
[root@localhost ~]# cut -d":" -f 1-3 /etc/passwd
[root@localhost ~]# cut -c 1,3,5 /etc/passwd
[root@localhost ~]# cut -c 1-5 /etc/passwd
sort 排序
[root@localhost ~]# sort aa.txt 默认情况下按首字符排序
[root@localhost ~]# sort -n aa.txt -n 按整个数字排序
[root@localhost ~]# sort -n -r aa.txt -r 逆序
[root@localhost ~]# sort -n -u aa.txt -u 去重 unique
[root@robin ~]# sort -t: -n -k3 /etc/passwd 按第三个字段排序
uniq 去重
[root@localhost ~]# uniq aa.txt 默认去掉连续的重复行
[root@localhost ~]# uniq -d aa.txt 只显示重复行 -d
[root@localhost ~]# uniq -d -c aa.txt -c 统计重复次数
[root@localhost ~]# uniq -u aa.txt 显示不重复的行 -u
grep 过滤
[root@localhost ~]# grep root /etc/passwd
[root@localhost ~]# grep ^root /etc/passwd
[root@localhost ~]# grep halt$ /etc/passwd
[root@localhost ~]# grep ^root$ aa.txt
[root@localhost ~]# grep -x root aa.txt -x 完全匹配
[root@localhost ~]# grep -v root /etc/passwd -v 取反
[root@localhost ~]# grep -n root /etc/passwd -n 行号
[root@localhost ~]# grep -i root /etc/passwd -i 忽略大小写
[root@localhost ~]# grep -rl root /etc/ -r 递归 -l列出文件名
[root@localhost ~]# grep -B 2 'root' /etc/passwd -B before
[root@localhost ~]# grep -A 2 'root' /etc/passwd -A after
[root@localhost ~]# grep -C 2 'root' /etc/passwd -C
[root@localhost ~]# echo '123' | tr '2' 'x'
常用练习题
1.统计你当前系统中可登录用户的数量
[root@localhost ~]# grep -c "/bin/bash" /etc/passwd
[root@localhost ~]# cut -d: -f 7 /etc/passwd | grep bash$ | wc -l
[root@localhost ~]# cut -d: -f 7 /etc/passwd | grep bash$ | uniq -d -c
[root@localhost ~]# grep bash$ /etc/passwd | wc -l
2.求passwd文件中uid最大用户的名字
[root@localhost ~]# grep cut -d: -f3 /etc/passwd | sort -n | tail -1 /etc/passwd | cut -d: -f 1,3
[root@localhost ~]# sort -t: -k3 -n /etc/passwd | tail -1 |cut -d: -f 1
3.求group文件中gid最小的组名和gid
[root@localhost ~]# grep cut -d: -f3 /etc/group | sort -n | head -1 /etc/group | sort -t: -k3 -n |head -1| cut -d':' -f 1,3
[root@localhost ~]# sort -t: -k3 -n /etc/group |head -1 |cut -d: -f 1
4.求系统中ens33的ip地址 例: ifconfig ens33 | awk '/netmask/{print $2}'
[root@localhost ~]# ifconfig ens33 | head -2 | tail -1 | cut -d' ' -f10
[root@localhost ~]# ifconfig ens33 | grep broadcast | cut -d' ' -f10
5.求出系统中所有网卡的ip地址 (ifconfig获取所有网卡信息)
[root@localhost ~]# ifconfig | grep netmask | cut -d' ' -f10
[root@localhost ~]# ifconfig | grep -B 1 netmask | cut -d' ' -f1,10
6.[root@localhost ~]# stat aa.txt
文件:"aa.txt"
大小:4 块:8 IO 块:4096 普通文件
设备:802h/2050d Inode:77530278 硬链接:1
权限:(0644/-rw-r--r--) Uid:( 0/ root) Gid:( 0/ root)
最近访问:2017-05-22 11:43:11.545941923 +0800
最近更改:2017-05-22 11:43:09.819870359 +0800
最近改动:2017-05-22 11:43:09.821870442 +0800
创建时间:-
取出
11:43:11
11:43:09
11:43:09
[root@localhost ~]# stat /root/aa.txt | grep + | cut -d' ' -f 2 | cut -d'.' -f 1
[root@localhost ~]# stat /root/aa.txt | grep + | cut -d'.' -f1 | tr ':' ' ' | cut -d' ' -f 1,5
查找命令
1.which
[root@localhost ~]# which cat
2.whereis
[root@localhost ~]# whereis cat
3.locate
[root@localhost ~]# locate anaconda-ks.cfg
[root@localhost ~]# updatedb 更新数据库
4.find
文件名
[root@localhost ~]# find / -name useradd
文件类型
[root@localhost ~]# find / -type f
1.
用户和组
[root@localhost ~]# find / -name rose 按用户
[root@localhost ~]# find / -group hr -ls 按组
[root@localhost ~]# find / \( -user natansha -a -group hr \) -ls -a 表示 与 and
[root@localhost ~]# find / \ ( -user natansha -o -group hr \) -ls -o 表示 或 or
[root@localhost ~]# find / -user natansha -a -type d
[root@localhost ~]# find / -nouser -ls 无用户文件
[root@localhost ~]# find / -nogroup -ls 无组文件
[root@localhost ~]# find / -nouser -o -nogroup
[root@localhost ~]# find / \( -nouser -o -nogroup \) -exec rm -rf {} \; 删除系统中没有用户或者没有组的文件
-exec 查找后执行
{} 引用 find找到的文件完整路径
\; 表示命令结束
[root@localhost ~]# find / ( -nouser -o -nogroup ) -ok rm -rf {} ;
-ok 交互式子
大小
[root@localhost test]# find /tmp/test/ -size 30M
[root@localhost test]# find /tmp/test/ -size +30M 大于30M但不等于
[root@localhost test]# find /tmp/test/ -size -30M 小于30M但不等于
[root@localhost test]# find /tmp/test/ \( -size +15M -a -size -45M \)
[root@localhost test]# find /tmp/test/ \( -size +15M -o -size -45M \)
[root@localhost test]# find /tmp/test/ \( -size +45M -o -size -15M \)
[root@localhost test]# find /tmp/test/ \( -size +45M -a -size -15M \) 匹配不到
排除/mysql /yum /mnt目录查找大于20M的文件
[root@localhost /]# find / -path "/yum" -prune -o -path "/mysql" -prune -o -path "/mnt" -prune -o -size +20M
按时间查找
访问时间 access time atime
如果actime慢于mtime 查看文件则更新atime,如果atime快于mtime查看文件则不更新atime
修改时间 modify time mtime
修改内容 mtime更新, 由于大小改变ctime也有更新
属性变化时间 change time ctime
拥有者,所属组,权限,大小,时间等
[root@localhost ~]# touch -d "2022-10-10 10:10:10" cc.txt 修改mtime
[root@localhost ~]# touch -a "2022-10-10 10:10:10" cc.txt 修改访问时间,同时ctime也改
[root@localhost ~]# touch -c -d "2022-10-10 10:10:10" yy.txt 如果文件存在则修改mtime 如果不存在则不创建
[root@localhost test]# find /tmp/test/ -mtime 5 查找距离今天5天的文件
[root@localhost test]# find /tmp/test/ -mtime +10 查找10天以前的文件
[root@localhost test]# find /tmp/test/ -mtime -10 查找10天以内的文件
按硬连接数查
[root@localhost ~]# find / -links 5 -ls
按权限找
[root@localhost ~]# find / -perm 777 -ls 完全匹配
[root@localhost test]# find /tmp/test -perm -420 -ls 每组权限必须包含查找权限
shell脚本举例
linux中不同扩展名判断文件类型,通过内容判断类型
在linux中通过x权限来确定是否是可执行程序

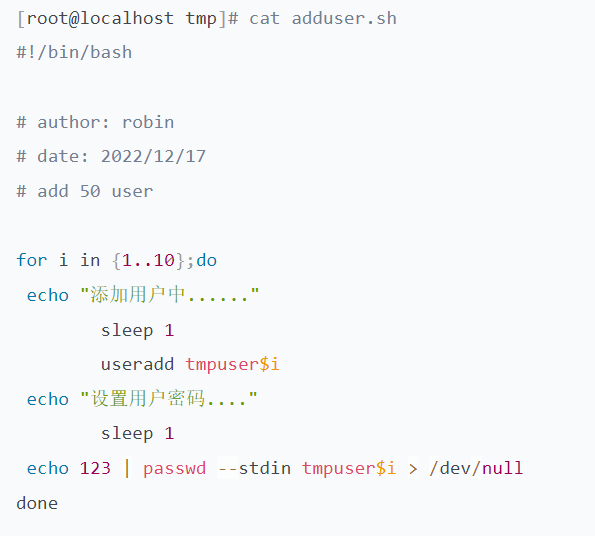 > >> 定向符 1 2 文件描述符fd 0标准正确输入 1 标准正确输出 2标准错误输出
> >> 定向符 1 2 文件描述符fd 0标准正确输入 1 标准正确输出 2标准错误输出
1> 标准正确输出,如果文件存在则覆盖,如果文件不存在则创建
1>> 标准正确输出,如果文件存在则追加,如果文件不存在则创建
2> 标准错误输出,如果文件存在则覆盖,如果文件不存在则创建
2>> 标准错误输出,如果文件存在则追加,如果文件不存在则创建
&> 标准正确和标准错误同时输出,如果文件存在则覆盖,如果文件不存在则创建
&>> 标准正确和标准错误同时输出,如果文件存在则追加,如果文件不存在则创建
快捷键
tab键补齐: 补齐命令 补齐文件
[root@localhost ~]# yum install bash-completion.noarch 补齐命令
[root@localhost ~]# history 显示执行过的历史命令(默认最近1000条)
[root@localhost ~]# !800 再执行一次第800条指令
[root@localhost ~]# !! 再执行一次上一条命令
[root@localhost ~]# !sys 再执行最后一条以sys开头的命令
xshell中
ESC键+. 引用上一条命令的最后一个参数
系统中
alt键(按住)+. 引用上一条命令的最后一个参数
$_ 表示上条命令最后一个参数
alt+1..5 表示1-5个xshell终端窗口
Bang(!)命令
!! :执行上一条命令。
^foo^bar :把上一条命令里的foo替换为bar,并执行。
!wget :执行最近的以wget开头的命令。
!wget:p :仅打印最近的以wget开头的命令,不执行。
!$ :上一条命令的最后一个参数, 与 Alt - . 和 $_ 相同。
!* :上一条命令的所有参数
!*:p :打印上一条命令是所有参数,也即 !*的内容。
^abc :删除上一条命令中的abc。
^foo^bar :将上一条命令中的 foo 替换为 bar
^foo^bar^ :将上一条命令中的 foo 替换为 bar
!-n :执行前n条命令,执行上一条命令: !-1, 执行前5条命令的格式是: !-5
查找历史命令
Ctrl – p :显示当前命令的上一条历史命令
Ctrl – n :显示当前命令的下一条历史命令
Ctrl – r :搜索历史命令,随着输入会显示历史命令中的一条匹配命令,Enter键执行匹配命令;ESC键在命令行显示而不执行匹配命令。
Ctrl – g :从历史搜索模式(Ctrl – r)退出。
控制命令
Ctrl – l :清除屏幕,然后,在最上面重新显示目前光标所在的这一行的内容。
Ctrl – o :执行当前命令,并选择上一条命令。
Ctrl – s :阻止屏幕输出
Ctrl – q :允许屏幕输出
Ctrl – c :终止命令
Ctrl – z :挂起命令
